Roohealthcare.com – If you’re looking for information on the Vertebral Parts of the Human Body, this article will help you to learn more about the different bones that make up the human spine. The information in this article will help you to understand the different bones and how they fit together. By the end of the article, you should have a basic understanding of vertebral parts and their functions. Let’s take a closer look at these bones.
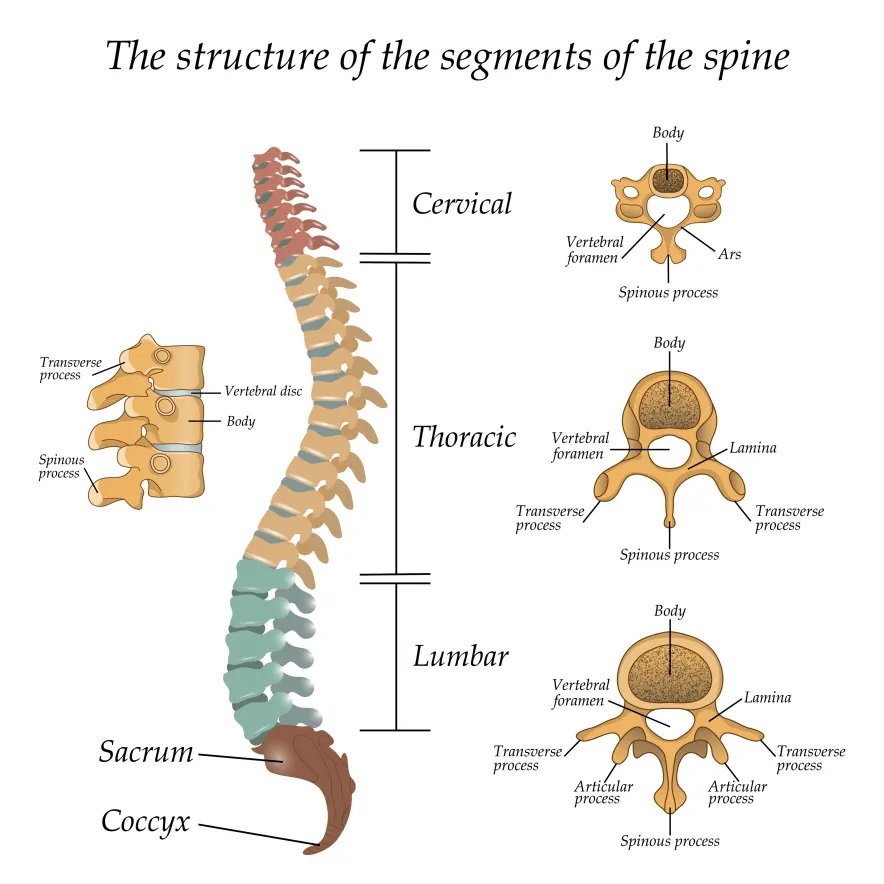
Typical Vertebrae Consists of Vertebral Arch
A typical vertebra is comprised of the vertebral arch, which is a series of paired laminae and pedicles. These bones then join together in the vertebral arch with transverse processes. Transverse processes are angled in relation to the spinous process and serve as anchors for the surrounding muscles. In addition to the laminae, each vertebra has four facet joints. These joints are what provide stability to the spine.
A vertebra’s endplates and pedicles form a cylinder-shaped arch that protects the spinal cord. Pedicles form the bridge between the front and back parts of a vertebra. Spinous processes are bony projections on the ends of each vertebra, which form the backside of the spinal cord. Spinous processes are attached to the pedicles above and below with ligaments. Sometimes the pedicles or spinous processes do not exist in the cervical spine.
The atlas is the largest cervical vertebra, C1; it is the first. The axis is shaped like a tooth, and the dens, or “dens,” is the second cervical vertebra. Both Atlas and Axis are responsible for rotation of the head, and the C3 through C7 are shaped like a box. The cervical vertebrae are separated by a transverse ligament.
Veretebra is Divided into Five Regions
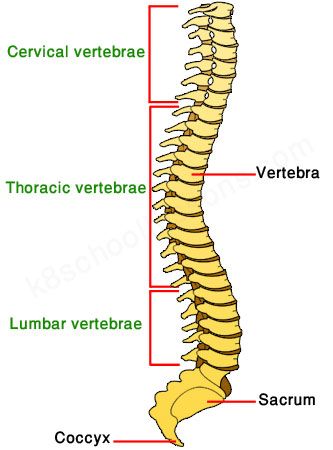
Each vertebra is made up of a bony structure called the vertebral body. The vertebrae are divided into five regions, each with its own characteristics and functions. The vertebrae of the neck articulate with the ribs while the lumbar and sacral vertebrae are much larger than those in the lower back. The top two cervical vertebrae of the neck articulate with the ribs. The sacrum is the largest of the five vertebrae and has a rounded spinous process.
In addition to vertebral parts, each segment has a name. The sacral spine consists of five fused vertebrae. Each segment has four or five foramina. The coccyx is a third or fourth cervical vertebral segment. The thoracic spine consists of 12 spinal segments, and incorporates the twelve ribs. The lumbar spine is the largest of the vertebral segments.
The three most important parameters of the vertebral body are its width, depth, and anterior and posterior height. These three components determine the kind of motion that can be achieved in each vertebral part. The vertebral column is 71 cm long in males and 61 cm in females. If you are experiencing pain or limited mobility, physical therapy is often the first choice of conservative treatment. By educating yourself on vertebral anatomy and kinesiology, you will be on your way to a fuller understanding of the human body.
Different Bone Combinations
The three spinal parts are made up of different combinations of bones. The vertebral column structure is determined by the shape of these bones. While the normal shape of the vertebral column is “S”-shaped from the side, the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines all curve slightly inward. The lower part of the spine supports most of the body weight and relies on the strength of the other two segments to function.
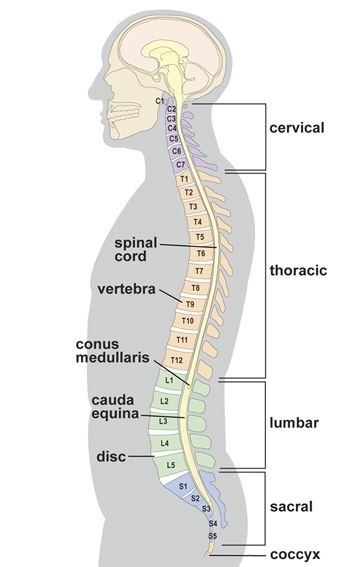
The human vertebral column has 33 vertebrae. It is further divided into three regions: the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar. The cervical vertebrae are named C1 and C2, and are the two bones that articulate with the occipital condyles in the skull. The thoracic vertebrae, on the other hand, are designated T1-T12. Lumbar vertebrae are L1-L5 and make up the lower part of the human body.
In addition to the spinal cord, each vertebra contains several nerves. Each nerve branches from a specific vertebra, with the first root exiting between the T1 and T2 vertebrae. Ten pairs of nerves exit the vertebrae, while five pairs exit the lumbar spine. The nerve roots are grouped in three regions: the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral. The thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves branch out from the spinal cord.
Reference: