Roohealthcare.com – Ankle cartilage is a smooth, flexible tissue that lines the edges of the joints. It cushions the joints from impact and helps people move their ankles smoothly. Injuries to ankle cartilage can cause a great deal of pain and often require surgery to restore proper function. Read on for some of the causes and treatment options for ankle cartilage injuries. This article will discuss the most common causes and treatment options for ankle cartilage injuries.
The Best Treatment Options for Ankle Cartilage
One of the best options for patients who have failed to find relief from less invasive treatments is ankle cartilage repair. Symptomatic treatment may include physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, steroid injections, and braces. However, patients whose ankle cartilage has severe damage may require a bone and cartilage transplant. In this case, a doctor will break the ankle bone to access the damaged area. After the bone and cartilage transplant, a patient can resume daily activities.
Ankle cartilage is comprised of the same type of cells as other articular cartilages, but it is characterized by a different biochemical composition and physiology. Because it is subject to a greater risk of PTOA, early diagnosis is crucial for preventing OA. Early detection of a cartilage damage may result in its onset in the subclinical phase. In the end, early treatment can prevent cartilage breakdown and osteochondral lesions.
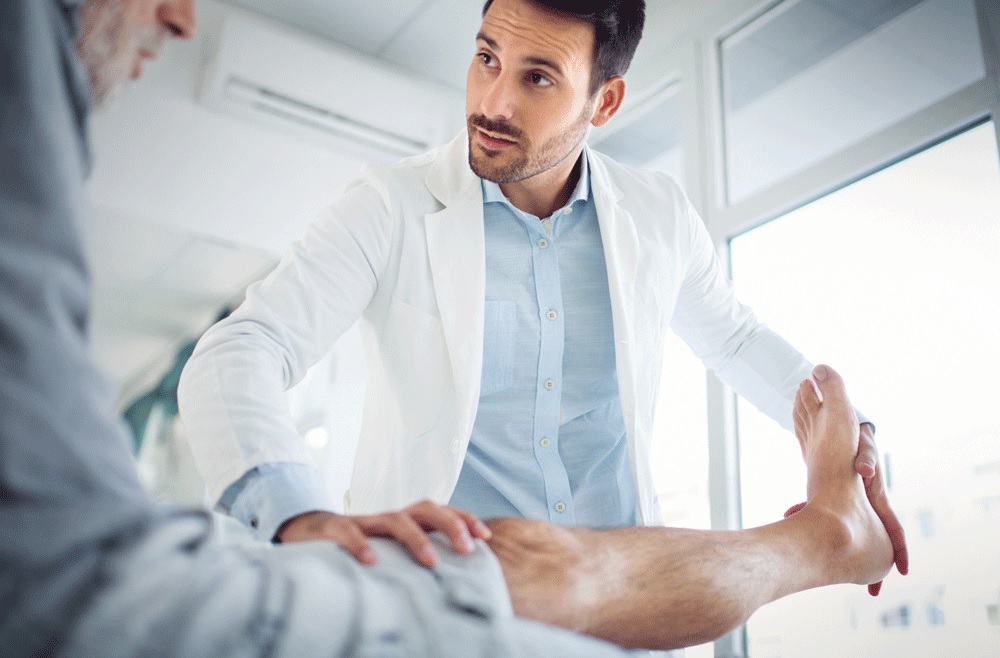

Ankle cartilage lesions may be pain or swelling inside the ankle joint. Patients may also experience clicking or catching sounds when walking, or they may experience swelling. The treatment for these conditions varies depending on where they are located in the ankle. The initial stages may require conservative management through rest and non-surgical options. Surgical procedures may be needed in more severe cases. If the lesions are too large, however, an ankle replacement may be necessary.
Stem Cells are a Promising Treatment
Another treatment option for ankle cartilage inflammation is stem cell therapy. Stem cells are a promising treatment. These cells are pluripotent, meaning that they can differentiate into multiple types of tissue. Ankle stem cells are harvested from bone marrow, and injected to a specific location where cartilage has been damaged. Ankle stem cells are then regenerated through targeted physiotherapy. The procedure can take anywhere from two to seven days.
A healthy joint needs exercise. Ankle cartilage damage does not, however, respond well to exercise. Overuse of high-impact sports can actually worsen cartilage damage. Therefore, moderate “load” activities protect the cartilage. High-impact sports such as running may add to the damage, so reducing the intensity of these activities will benefit the ankle cartilage. Additionally, it is best to avoid extreme sports such as tennis, basketball, running, and gymnastics.
Ankle cartilage surgery can help a patient return to activity. In some cases, this type of procedure will involve a minimally invasive procedure known as arthroscopic surgery. In this procedure, small holes are made in the bone at the base of the crater of the damaged cartilage. Blood trickles up through these holes, creating a blood clot that will eventually turn into fibrocartilage. After recovery, patients can begin to exercise or participate in other athletic activities.
Causes of Ankle Injury and Joint Inflammation
Ankle injuries are often caused by a variety of factors. Inflammatory conditions can affect ankle cartilage, which causes discomfort. Ankle injuries and arthritis are commonly caused by cartilage damage. This sets the stage for the next stage of damage. Acute injuries and pain can also result from an injury to the ankle. To prevent this from happening, it is important to understand how the ankle works. Fortunately, treatment options for ankle pain are available.
Ankle arthritis typically affects younger patients, and is less common than other types of arthritis. Patients with this condition are usually younger than people with arthritis in the hip. Trauma causes ankle arthritis. Ankles that aren’t straight can cause overstressing of the ankle bones and result in inadequate weight-bearing. The mechanical overstressing of the ankle joints can lead to the development of osteoarthritis.
Another complication of ankle replacement is bone erosion. This is a result of tiny plastic particles rubbing against bone tissue. If you suffer from this problem, your surgeon may recommend bone grafting or a surgical procedure to replace the ankle cartilage. There are a number of potential complications associated with ankle replacement, including fractures of plastic components, bone spurs, and loosening of metal parts. The ankle joint can be permanently reconstructed, but if you experience the same problems again, your ankle may need to be replaced again.