Roohealthcare.com – You’ve probably heard of the Suprascapular Muscle, but you don’t know what it is or how it works. This article aims to answer those questions, and to give you some tips for strengthening your suprascapular muscle. Then, you can follow the steps in this article to help you get back to work, or improve your sports performance. If you are interested in learning more about the Suprascapular Muscle, continue reading.
Diagnostic Exam is Necessary
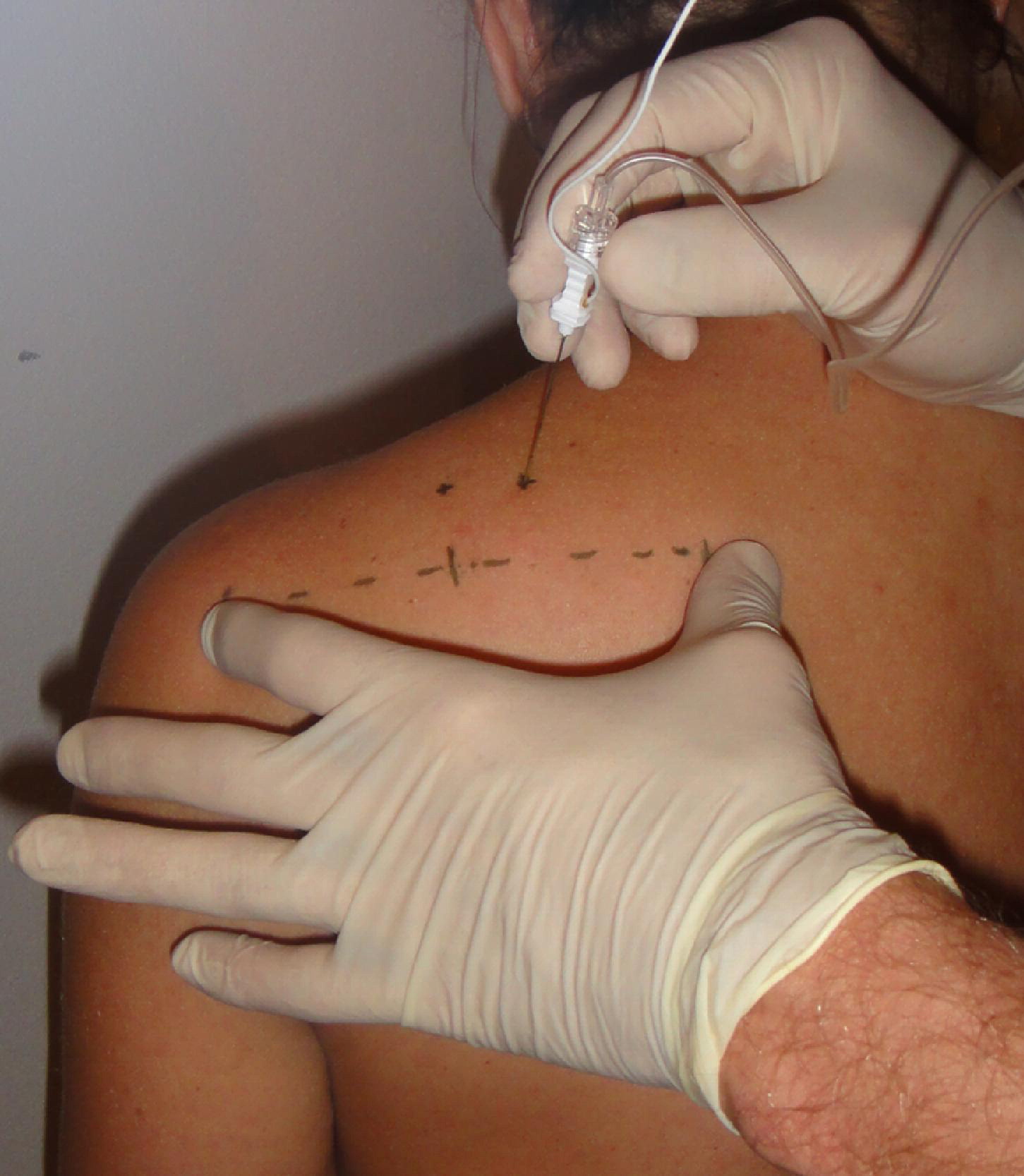
First, a diagnostic exam is necessary. The clinician must confirm the existence of suprascapular entrapment. This is done by making an incision on the skin 3 cm medial to the posterolateral corner of the acromion. Next, the clinician must make an incision along the spinoglenoid notch. In this step, the anterior coraco-scapular ligament is split and the infraspinatus muscle belly is dislocated. Next, the spinoglenoid ligament is cut from the edge of the scapular spine. The nerve is then released from the notch by using scissors proximally and inferiorly.
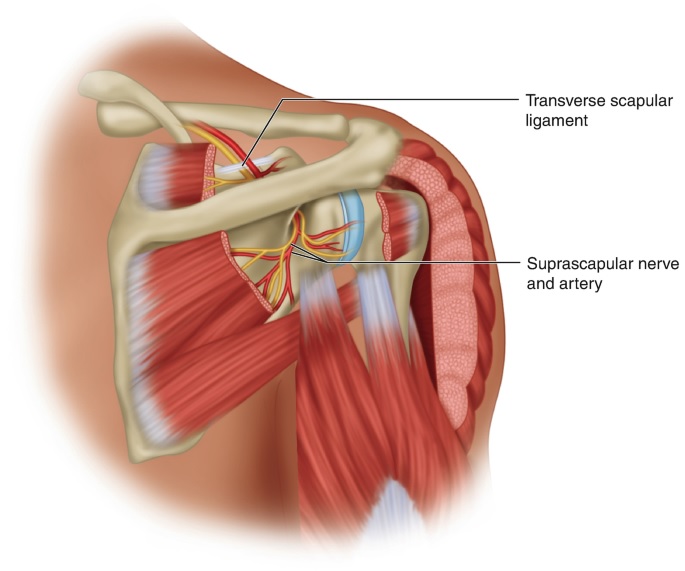
The suprascapular nerve is located in the scapula. In cadaveric shoulders, it passes beneath the superior transverse scapular ligament. Specifically, it lies near the superior border of the anterior coracoscapular ligament. In both cases, the nerves of the suprascapular foramina are found. This implies that the suprascapular nerve is more closely related to the right shoulder.
Neuropathy of the suprascapular nerve can affect the infraspinatus muscle. This causes weakness and pain in overhead arm movements. The muscle can deteriorate under pressure, and can even lead to chronic neuropathic shoulder pain. However, EMG and nerve conduction velocity are not 100% accurate for diagnosing suprascapular entrapment. If you are experiencing neuropathic shoulder pain, you should seek medical attention immediately.
Understanding the Functions of the Suprascapular Nerve
In order to understand the function of the suprascapular nerve, you must know where it is located. The area between the superior transverse scapular ligament and the anterior coracoscapular ligament is the suprascapular opening. The notch itself has several morphological features that help you understand where this nerve originates. Its morphology can help you understand which areas of the brain are controlled by this muscle.
Surgical intervention to relieve the pain caused by the entrapment of the suprascapular nerve is one of the most effective treatments for this problem. In fact, surgical intervention can correct this problem, but the time between onset of symptoms and surgery is critical. The surgical procedure will depend on the pathology of the nerve that was compressed. In order to properly diagnose the condition, you must have studies of the suprascapular muscles and nerve.
The surface area of the suprascapular opening was measured using a digital calliper. In type I specimens, the suprascapular opening area was 30.9 mm2. Then, the two-part measurements of the suprascapular foramen were calculated with a digital calliper. The areas of the suprascapular opening were then calculated in twenty specimens by one researcher and by a second researcher. Finally, the central thickness of the ossified ligaments was measured using the same method.
Diagnosis of Suprascapular Muscle Pain and its Causes
The diagnosis of Suprascapular Muscle Pain is crucial. It must be ruled out if the pain is due to an underlying condition such as a tendon or rotator cuff tear. In case of this condition, the patient should undergo an MRI. Furthermore, the condition can co-exist with other shoulder pathologies, such as radiculopathy. Therefore, it is essential to evaluate all patients who suffer from shoulder pain and perform overhead activities.
In case of a ruptured suprascapular muscle, surgical treatment should be performed to repair the nerve. Non-operative treatment should be considered if the patient’s condition is not associated with atrophy, but instead is accompanied by weakness and pain. The surgeon will have to examine the muscles to make sure they aren’t tangled. When the patient is stable, he or she should be able to do passive exercises immediately after the operation.
A successful procedure for the suprascapular nerve PRF results in effective pain relief and improved function in the shoulders of patients. The study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and an FDA approved protocol was used. Patients in the study must have refractory shoulder pain, be unresponsive to conservative treatments, and have a radiologically proven partial tear of the rotator cuff. If you’re suffering from pain and a limited range of motion, this procedure may be right for you.