Roohealthcare.com – A subretinal injection is performed to treat retinal detachment. The subretinal injection involves injecting a bolus of cells under the diametrically opposed retina. Once the injection has taken place, the cells can be visualized through a confocal scanning ophthalmoscope. Labeling the RPE cells with a fluorescent marker allows for precise measurement of the retinal detachment induced by the injection.
New Method for Precise Location for Retina Injection
IntactEye is a new method that allows a precise location for retinal injection. Using two orthogonal images of the retina, the program maps the exact location of the injection. The system allows for a 3D map of the eye and is also compatible with laser-based retinal surgery. It is an excellent alternative to laser resection. It is safer than the former and may reduce the risk of vision loss.
Pre-retinal injections were performed using a blunt-tip syringe and a 27G trocar blade. The needle is 12 mm long, blunt-ended, and connected to a 100-mL Hamilton syringe. The intraocular pressure should return to normal before the procedure is completed. Injecting the RPE cells into the eye is a complicated procedure, but it is an essential part of treating detachment.
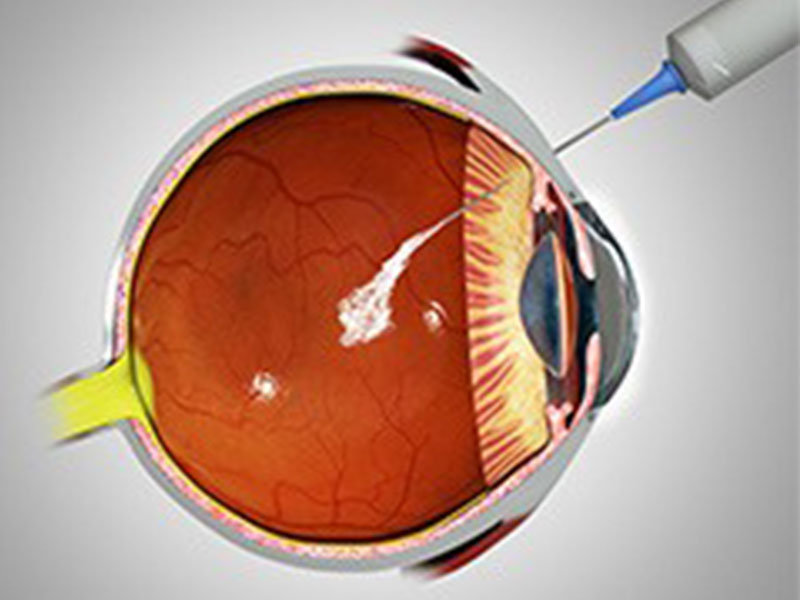
After the procedure, a 30-gauge needle attached to a 1-ml syringe is used to inject the VB. After the injection, the needle is angled tangentially on the globe and a small amount of pressure is applied until an internal distortion is visible. After the injection, the dye is drained out of the eye through the break site. There are several risks associated with the trans-scleral injection.
Risks of Retinal Detachment Post-Injection
There is also a risk of post-injection retinal detachment. This happens more often in patients over forty, those with advanced eye disease, and those with high myopia. The rate of this complication depends on the surgical technique used. An injection by a poorly trained doctor is a higher risk. Early detection of retinal detachment is the key to successful management. Floaters are indicators of a retinal break and should be investigated.
Retinal injections are expensive, so a practice needs to track them effectively. Injection medication is costly, and even a few missed doses can affect reimbursement. ArbiMed Retina is a useful tool for capturing information about patients’ previous treatments. It also notes expiration dates and lot numbers for injection medications. This will help assign proper doses and select patients accordingly. The software is also helpful in the selection of patients.
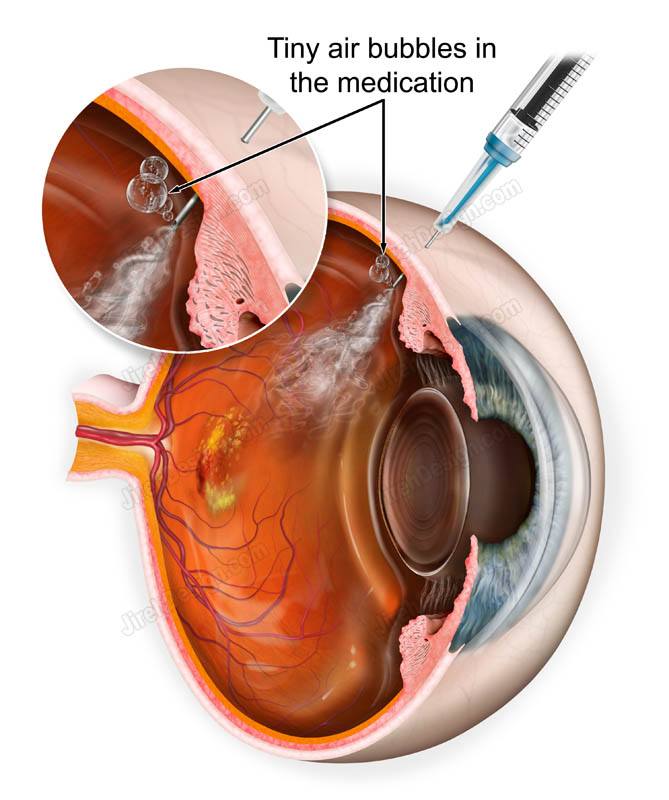
After a pre-retinal injection, AAV transduction efficiency was significantly increased, with a significant increase in transduced photoreceptor cells. The transduction efficiency varied depending on the retinal area injected. Some areas of the retina showed a significant amount of transduction, while others displayed minimal involvement of ONL. Furthermore, some areas showed very strong transduction of the GCL and INL, with minimal involvement of the inner retina.
Proven Effective Treatment Options
A pre-retinal injection is also a promising option. Pre-retinal injection involves advancing the injection cannula beyond the vitreous body, with the tip inserted into the space between the ILM and the posterior hyaloid membrane. This procedure is completely safe, and it is already being used in several animal studies. In addition to reducing the risk of vision loss, this technique has been shown to be effective for the treatment of retinal detachment.
One study also showed that the procedure of subretinal injection is a relatively easy procedure for animals. However, many procedures are complicated, and it is important to ensure that the procedure is performed by a skilled physician. To avoid complications, the procedure should be performed under a certified doctor who has completed extensive training. The study included Wistar rats and was conducted under all the ARVO guidelines. The rats were injected with 10 ml saline via the limbal entrance. The procedure was recorded and data were analyzed.
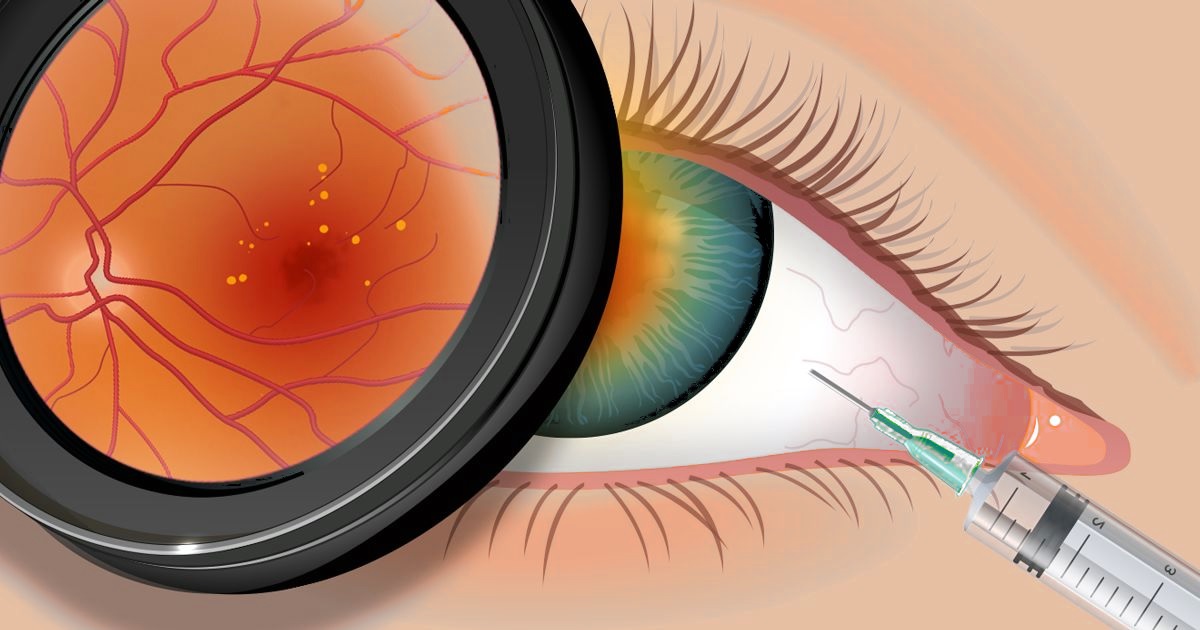
One side effect of the intravitreal retinal injection is the detachment of the posterior hyaloid membrane. While this is rare and usually causes minimal discomfort, it does not affect visual acuity. In fact, posterior hyaloid membrane detachment is an inevitable side effect of age and various retinal diseases. Therefore, a subconjunctival injection will not impact visual acuity.
Reference: