Roohealthcare.com – Open fractures are often classified by the Gustilo-Anderson classification system, which takes several factors into consideration. Type I open fractures are those with minimal damage and comminution, whereas Type II are those with moderate to high levels of soft-tissue damage. Type III fractures, on the other hand, are those with moderate to high levels of comminution and significant soft-tissue damage. In addition to these differences, open fracture treatment must be personalized to each individual patient.
Open Fractures Present Significant Risk
Open fractures present significant risks. In addition to bone and soft tissue damage, open fractures are prone to infection, limb dysfunction, and multiple organ failure. Patients with open fractures must undergo a comprehensive evaluation and treatment plan by a trained medical team. This may include a diagnostic imaging procedure and laboratory studies to help determine the best course of treatment. In addition to assessing the risks associated with open fractures, it is important to know how to properly clean and irrigate an open wound to ensure the healing process.
One important component of open fracture treatment is antibiotics. When used properly, antibiotics can reduce the risk of infection by six times. Lack et al. studied the effects of antibiotics after 66 minutes of injury. When given within three hours of the fracture, the risk of infection fell to zero, while if given after that time, the risk increased to 17%. Antibiotics are crucial for open fracture treatment, but patients should be aware of the fact that these breaks take longer to heal than other types of fractures.
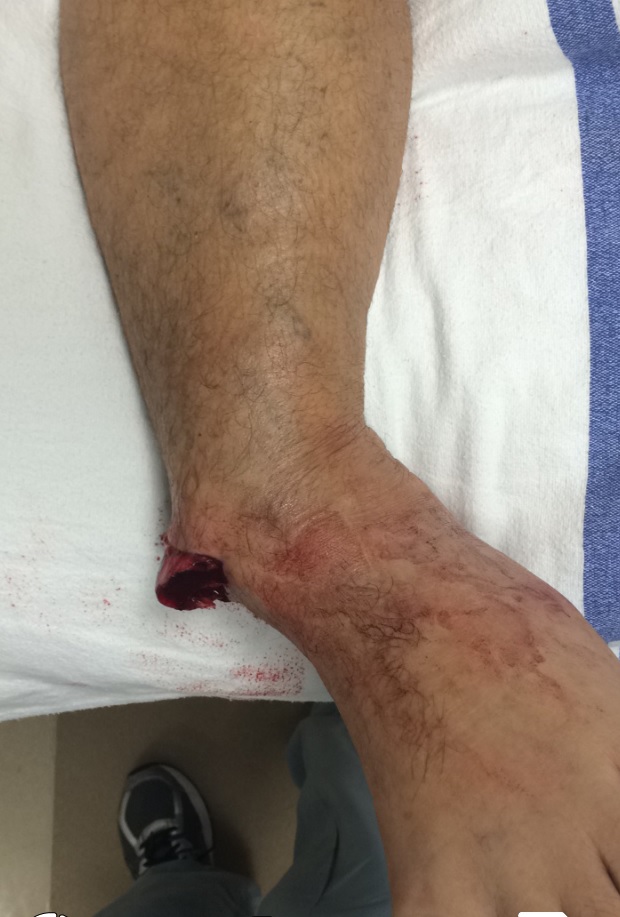
Surgical cleaning of the bone is one of the first steps in open fracture treatment. In addition to the surgical repair, irrigation is also a part of the treatment. This is normally performed in the operating room under general anesthesia, though there are some cases where patients may be unable to receive anesthesia. If resuscitation is not enough, this step may be necessary. Moreover, an open fracture may require the use of a surgical graft.
Early Antibiotics Can Reduce the Risk of Infection
A recent study reviewed 70 open fractures and concluded that the early administration of antibiotics reduced the risk of infection. This study also concluded that the amount of time between the fracture and the debridement in the operating room did not influence infection rates. In another study, Bednar and Parikh analyzed 56 pediatric open fractures of the lower extremity caused by blunt trauma. They found that an antibiotic delay of more than six hours was associated with a 25 percent infection rate, while a delayed treatment caused a 12% infection rate in five of 42 patients.
A delayed debridement of open fractures did not increase the risk of infection. However, this principle has no direct impact on the occurrence of infection in open fractures. It is based on arbitrary thresholds. The sooner you start debridement, the less the chances of infection. So, it is important to avoid any delays. There is no definitive answer to this question. It is important to note that debridement is an essential part of the treatment of an open fracture, whether the patient has undergone surgery in the past.

The infection rate associated with open fracture surgery varies by type. For example, the time since the accident, fracture type, and soft tissue damage are all factors that can influence the likelihood of infection. In the study, a risk score was developed with these three variables and predicts the risk of infection at the initial evaluation. This scoring system had a sensitivity of 0.84 and a specificity of 0.54, with an area under the ROC curve of 6.5. This study suggests that prevention of infection is the most important measure of open fracture treatment.
Types of Open Fractures
There are several different types of open fractures and many different fixation methods can be used to repair these injuries. While some methods are better than others, there is no clear answer for which one is the best for you. There are several types of surgery, including open fractures, which can help minimize the risks of infection and provide a stable fracture fixation. It is important to determine the type of treatment before making any decisions. If you don’t feel comfortable having surgery, consult a surgeon before making a final decision.
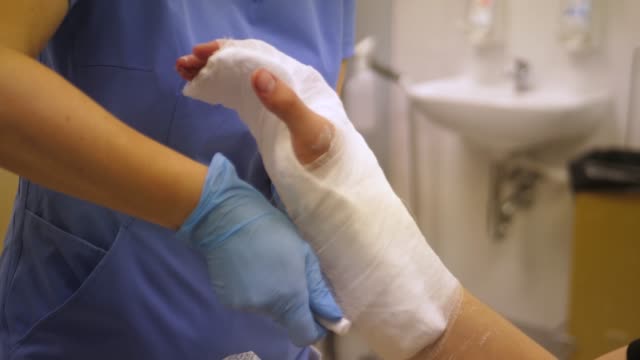
A recent study examined the relationship between the time of delay in debridement and deep infection rate in open fracture patients. The researchers examined 364 consecutive open fracture patients from an academic level one trauma center in North America. They noted that the two outcomes were related, and that the longer a patient waited before undergoing debridement, the greater the risk of developing a deep infection. The study concluded that a patient’s risk of developing a deep infection increased by 3% per hour of delay in treatment.
Reference: