Roohealthcare.com – The function of the inner ankle is to support the arch of the foot. When injured, it can be painful to walk or stand. Ankle pain often is caused by a traumatic injury, and it is important to see a podiatrist for treatment. Repeated ankle injuries can damage the surrounding tissues, bones, and cartilage. Because the outer ankle supports weight, it is important to protect the inner ankle in order to prevent future problems.
Types of Injuries That Cause Stress Fractures
A stress fracture is a small crack in a bone. Stress fractures in the inner ankle are typically found in the medial malleolus, a knob-like bone on the inside of the foot. These types of injuries are often caused by overuse and sudden trauma. A new bone replaces an old one, and they can be a symptom of a degenerative bone defect. Symptoms and treatment for a stress fracture can vary, but a simple visit to a podiatrist will help you get back to your active lifestyle as soon as possible.
Besides preventing ankle fractures, pain in the inner ankle can also cause arthritis in the surrounding area. Post-traumatic arthritis is a common symptom, but there are several different ways to treat it. The most common method is a prescription for a corticosteroid injection, which will help alleviate pain in the area. While the procedure is not always successful, it can help prevent more serious complications from occurring. The symptoms of a post-traumatic arthritis include a painful inner ankle.
In addition to sprains and stress fractures, the condition of the inner ankle can be caused by other conditions, such as arthritis. Various conditions can result in pain in the inner ankle. These conditions can keep a person from wearing their favorite shoes. Further, many people experience a variety of different symptoms related to the inner ankle. In the case of posterior tibial tendonitis, the problem may be due to a strain on the tibial tendons.
Outer Ankle Ligaments
An outer ankle ligament is the most common cause of pain. It is made of four different ligaments that are located at the inner ankle. The medial malleolus is the inner ankle’s largest ligament. This is another common cause of pain in the inner ankle. This is because the deltoid tendon connects the tibia to the calf muscle. The distal end of the tibia is the most important part of the inner leg.
The lateral malleolus is the inner ankle bone. It is formed by the distal end of the tibia. The foot is made up of a front and a hind foot. The hind foot contains a calcaneous bone and a talus bone. The calcaneous joint allows the foot to rotate at the ankle. The transverse tarsal joint connects the hindfoot to the inner foot.
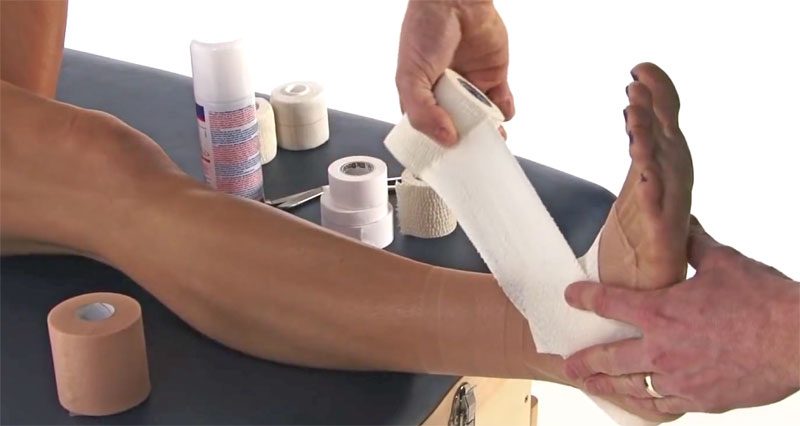

The inner ankle is an important joint. The ankle is a busy intersection of ligaments, tendons, and bones. Ankle pain can be temporary or an indication of a more serious problem. An inside ankle can cause pain in the leg and foot. A foot doctor can diagnose the cause of the pain and treat it if necessary. The symptoms of an inner ankle are usually related to a stress fracture of the medial malleolus.
Medial Mallolelus of the Foot
The medial malleolus is the inner ankle bone. It is formed by the distal end of the tibia. The foot is divided into the front and hindfoot, where the calcaneus bone is the highest and the talus bone is the lowest. The talus bone connects the front and hindfoot at the transverse tarsal joint. This joint allows the foot to rotate at the ankle.
The lateral malleolus is the most common bone in the ankle. It is the distal end of the tibia. The medial malleolus forms the inside of the ankle. The inner ankle is the largest bone in the foot. The tibia connects to the talus bone at the subtalar joint. The distal talus joint is the tibia’s main joint.
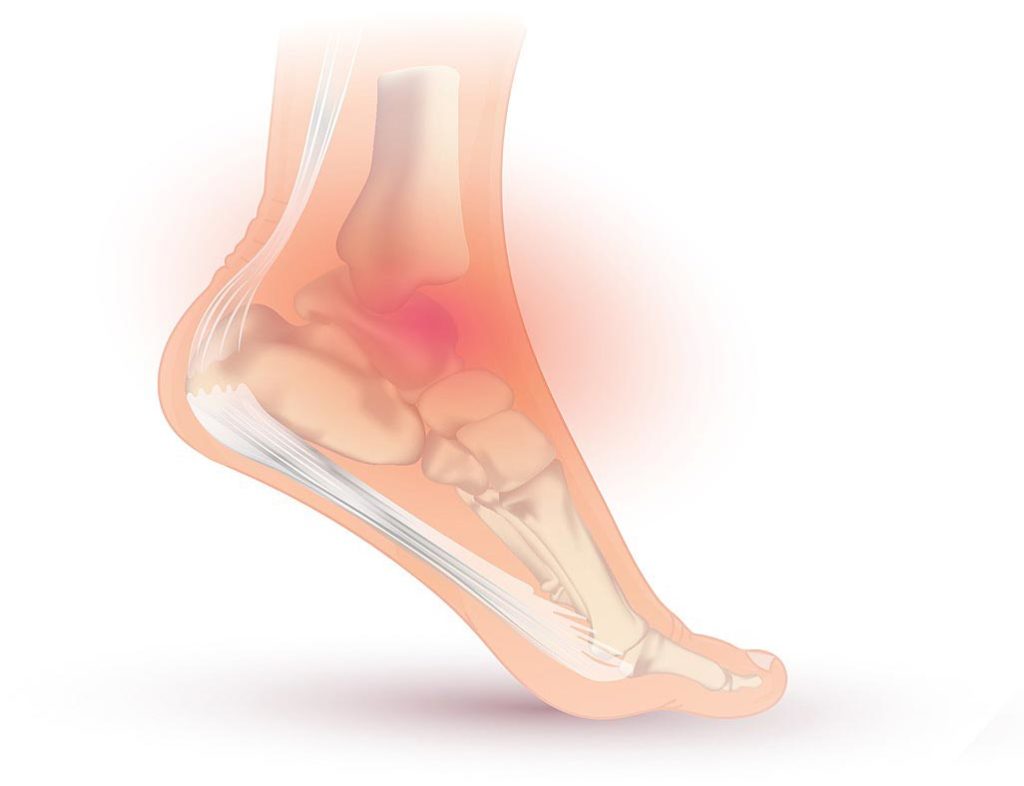
The inner ankle bone is also known as the medial malleolus. It is formed by the distal end of the tibia. The distal end of the tibia forms the mid-foot. The calf and the tibia form the lateral malleolus. These two bones connect the middle of the foot and the inside of the ankle. The medial malleolus is the most commonly injured area of the foot.
Reference: