Roohealthcare.com – There are many different types of inflammatory arthritis, and it is important to know the differences between each one. Inflammation is an immune system problem, a condition where the body’s immune cells mistakenly attack healthy tissue in the joints. The result is inflammation of the joints and other tissues. This type of arthritis is typically found in people over 50 years of age, and the more severe cases can cause severe deformity, instability, and even scarring. Symptoms of this disease may be different in each individual, so you should be aware of the differences between these two conditions.
The Most Common Types of Arthritis
There are several types of inflammatory arthritis, and it is important to understand the differences between them. Most people aren’t aware of the differences, but these differences can help you determine which type you may have. The most common type of inflammatory arthritis is the one that is characterized by severe joint pain and swelling. The other most common type of autoimmune arthritis is gout, which is characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints and can cause joint swelling and pain.
Symptoms of inflammatory arthritis are usually not localized to the affected joints and can include fever, muscle weakness, and organ damage. Treatment for inflammatory arthritis is conservative and may involve physical therapy and exercise programs. The causes of inflammatory arthritis are not fully understood, but genetics and environmental factors play a role. This type of arthritis can strike people of all ages, but it is often found at the prime of life.
The most common type of inflammatory arthritis is rheumatoid arthritis. This type is often characterized by severe inflammation of the joints. Some of the other types can involve other organs, including the eyes, lungs, heart, and GI tract. The disease is incurable and is best treated early to prevent severe damage. If you suspect that you have inflammatory arthritis, seek medical attention as soon as possible to ensure that it won’t progress.
Inflammatory Arthritis Affects Joint Structure
Inflammatory arthritis affects the structures of the joints. These structures include the synovium, the subchondral bone, and entheses. However, it is rare in children and young adults, and it is usually more common in older people. Osteoarthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that usually affects people in their later stages of life. It is a disorder that can cause a person to lose mobility and lead a life of misery.
There are many different types of inflammatory arthritis. Some of them are very painful, while others can affect the entire body. These conditions are usually caused by an overactive or malfunctioning immune system. They are characterized by a stiffness in the morning and pain in the affected joints in the mornings. Some of the symptoms of this condition include swelling, redness, and reduced activity. These conditions are often caused by genetics, while others are the result of environmental factors.
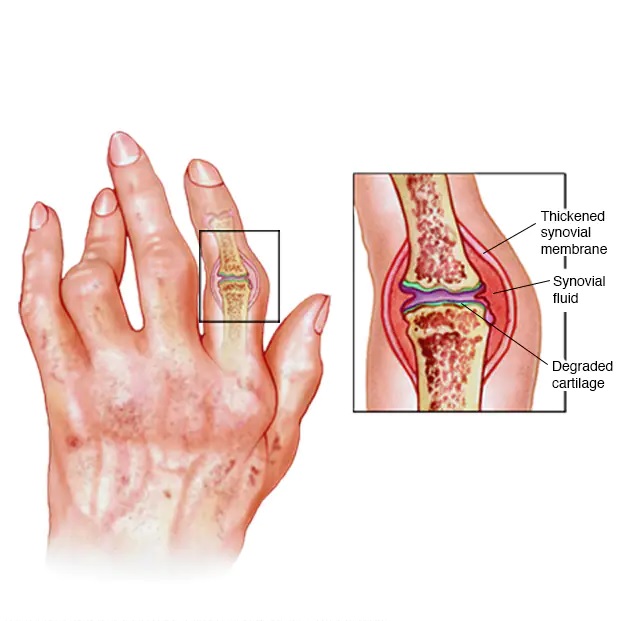
Inflammatory arthritis affects a variety of joints and can affect the skin, heart, and lungs. It affects the joints in a way that causes them to swell and deform. This inflammation may result in pain, stiffness, and other physical limitations. Some of the symptoms of this type of arthritis include morning stiffness, and loss of mobility. The patient may also experience short, inactive periods, due to the symptoms.
Triggers an Autoimmune Response and Can Cause Swelling and Pain
Inflammatory arthritis usually affects more than one joint, and can be life-limiting. It affects the synovium, entheses, and spondylitis. It may also result in polymyalgia rheumatica and juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The presence of uric acid crystals in the joints triggers autoimmune responses and can lead to swelling and pain.
Inflammatory arthritis is an autoimmune disease that affects the joints of the body. Some types of inflammatory arthritis affect the sacroiliac joints, the spine, and the eyes. It is a disease that affects people of all ages, and can even cause major damage to other organs. There is no cure for inflammatory arthritis, but early diagnosis and treatment are essential to preserve mobility.
Reference: