Roohealthcare.com – Symptoms of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity include fatigue, dizziness, joint pain, headaches, abdominal discomfort, and nausea. Treatment options include medications, exercise, and nutritional supplements.
Some Symptoms of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Symptoms of non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) can include nausea, headaches, joint pain and fatigue. They can also be accompanied by depression, anxiety and other ailments. Typically, non-celiac gluten sensitivity is diagnosed by elimination and observation protocols. Patients are advised to follow a gluten-free diet for 6-8 weeks. After this period, gluten-containing foods are reintroduced into the diet to determine the effects. Gluten is a protein found in grains. This protein has a chewy texture. When eaten, gluten causes inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. However, in the case of gluten intolerance, the intestinal damage is not as severe as it is in celiac disease.
Many people experience some of the same symptoms, including stomach pain, diarrhea and abdominal distension. Gluten intolerance can also be diagnosed through skin prick tests. The tests may also include blood tests and upper endoscopy procedures. Whether you are diagnosed with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, you should talk to your doctor to find the right treatment for you. A gluten-free diet may help you reduce symptoms. However, a temporary elimination diet should not be used without consulting with your medical team.

A diagnosis of non-celiac gluten sensitivity is not always made using the standard diagnosis criteria. The diagnosis is usually based on wheat allergy tests or a gluten challenge. A gluten challenge is usually performed by having the patient eliminate gluten for 6 weeks. After the diet is completed, the patient reintroduces gluten-containing foods. The duration of the gluten challenge may vary. If the symptoms improve, the diagnosis of non-celiac gluten senescence is considered confirmed.
Appropriate Treatment Options for Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Gluten challenge with crossover is the gold standard in gluten sensitivity diagnostics. The gluten challenge must be performed in a blinded environment. This allows for an objective diagnosis. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment options for non-celiac gluten sensitivity is important. It is a disease that causes damage to the small intestine and can affect a person’s health. Often, patients will notice improvement within days or weeks. However, if symptoms persist, more tests may be necessary.
If you think you have NCGS, you may want to try a gluten-free diet. This will help your small intestine heal. However, it is important to consult your doctor before starting the diet. Your doctor will provide you with advice and tests to ensure the diagnosis is correct. Your doctor may recommend a gluten challenge to confirm your diagnosis. This involves taking a sample of your intestinal lining. The challenge is usually blinded and placebo-controlled. The doctor will also ask you to record any symptoms you experience after you stop ingesting gluten.
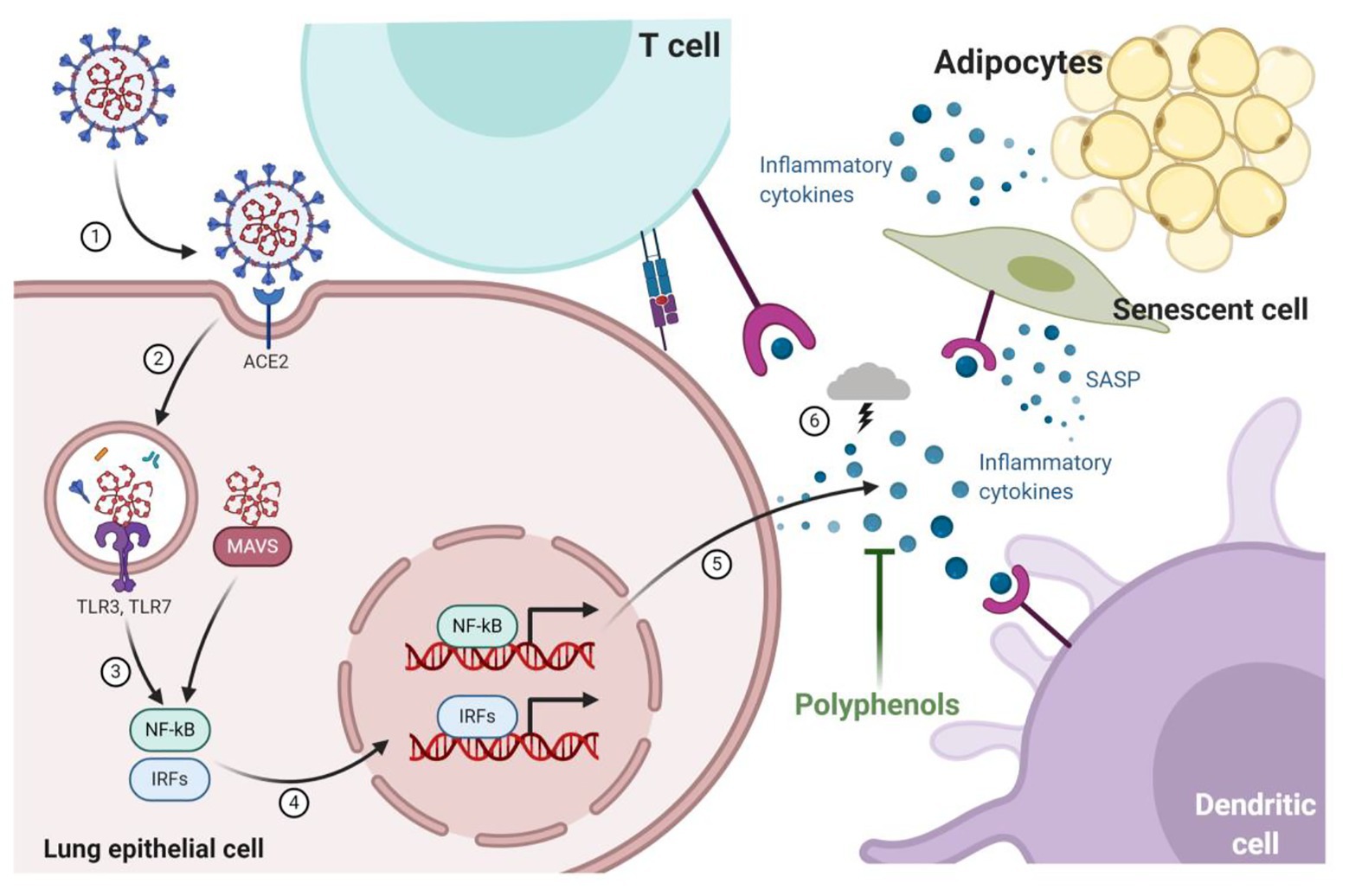
 Increasing your intake of polyphenols may help you manage symptoms of non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Polyphenols are a class of bioactive compounds that are found in a variety of foods and beverages. They are known for their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Polyphenols can also help maintain a healthy gut, preventing a variety of intestinal diseases.
Increasing your intake of polyphenols may help you manage symptoms of non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Polyphenols are a class of bioactive compounds that are found in a variety of foods and beverages. They are known for their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Polyphenols can also help maintain a healthy gut, preventing a variety of intestinal diseases.
Polyphenols Exercising Inhibitory Effects on Chemokines
A number of studies have shown that polyphenols are effective at inhibiting the release of cytokines that can trigger an immune response. Polyphenols also exert inhibitory effects on chemokines, microbial products, and signal transduction pathways. Polyphenols have also been shown to reduce inflammation and improve gut health in inflammatory bowel disease and gluten-related disorders.
There is some evidence that polyphenols can affect the permeability of the intestinal wall. They can also help protect the gut from oxidative stress. Polyphenols have been shown to improve the balance of Th17 and Treg cells. This may help to reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases and cardiometabolic disorders. Despite the common association between celiac disease and liver diseases, scientists are still unsure about the underlying mechanisms. Several factors may contribute to the link.
 The gut-liver axis is one such potential explanation. In patients with CD, a small intestinal barrier is compromised, permitting toxins to enter the bloodstream and contributing to hepatic injury. This increased intestinal permeability is believed to be an early feature of CD pathogenesis. Studies have shown that celiac patients are at high risk for liver damage and cirrhosis. Researchers have also shown that a gluten-free diet can reverse liver disease in these patients. In a study of four patients with liver failure, all four showed a rapid recovery after following a strict gluten-free diet. The liver abnormalities were reversed and liver enzymes normalized within six months. If you have and want to send articles to roohealthcare, you can visit this page!
The gut-liver axis is one such potential explanation. In patients with CD, a small intestinal barrier is compromised, permitting toxins to enter the bloodstream and contributing to hepatic injury. This increased intestinal permeability is believed to be an early feature of CD pathogenesis. Studies have shown that celiac patients are at high risk for liver damage and cirrhosis. Researchers have also shown that a gluten-free diet can reverse liver disease in these patients. In a study of four patients with liver failure, all four showed a rapid recovery after following a strict gluten-free diet. The liver abnormalities were reversed and liver enzymes normalized within six months. If you have and want to send articles to roohealthcare, you can visit this page!
Reference :
Roszkowska, Anna, et al. “Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: a review.” Medicina 55.6 (2019): 222.